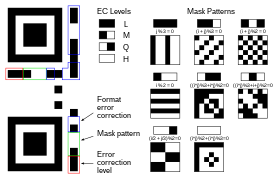QR code (abbreviated from
Quick Response Code) is the trademark for a type of
matrix barcode (or two-dimensional
barcode) first designed for the
automotive industry in Japan. A barcode is a machine-readable optical label that contains information about the item to which it is attached. A QR code uses four standardized encoding modes (numeric, alphanumeric, byte/binary, and
kanji) to efficiently store data; extensions may also be used.
[1]
The QR code system became popular outside the automotive industry due to its fast readability and greater storage capacity compared to standard
UPC barcodes. Applications include product tracking, item identification, time tracking, document management, and general marketing.
[2]
A QR code consists of black modules (square dots) arranged in a square grid on a white background, which can be read by an imaging device (such as a camera, scanner, etc.) and processed using
Reed–Solomon error correction until the image can be appropriately interpreted. The required data are then extracted from patterns that are present in both horizontal and vertical components of the image.
[2]
History[edit]
The QR code system was invented in 1994 by
Denso Wave. Its purpose was to track vehicles during manufacture; it was designed to allow high-speed component scanning.
[3] QR codes now are used in a much broader context, including both commercial tracking applications and convenience-oriented applications aimed at mobile-phone users (termed mobile tagging). QR codes may be used to display text to the user, to add a
vCard contact to the user's device, to open a
Uniform Resource Identifier (URI), or to compose an e-mail or text message. Users can generate and print their own QR codes for others to scan and use by visiting one of several paid and free QR code generating sites or apps. The technology has since become one of the most-used types of two-dimensional barcode.
[4]
Standards[edit]
There are several standards that cover the encoding of data as QR codes:
[5]
At the application layer, there is some variation between most of the implementations. Japan's
NTT DoCoMo has established
de facto standards for the encoding of URLs, contact information, and several other data types.
[7] The open-source "ZXing" project maintains a list of QR code data types.
[8]

A QR code used on a large billboard in Japan, linking to the sagasou.mobi website
QR codes have become common in consumer advertising. Typically, a
smartphoneis used as a QR code scanner, displaying the code and converting it to some useful form (such as a standard
URL for a website, thereby obviating the need for a user to type it into a
web browser). QR code has become a focus of
advertising strategy, since it provides a way to access a brand's website more quickly than by manually entering a URL.
[9][10] Beyond mere convenience to the consumer, the importance of this capability is that it increases the
conversion rate (the chance that contact with the advertisement will convert to a sale), by coaxing interested prospects further down the
conversion funnel with little delay or effort, bringing the viewer to the advertiser's website immediately, where a longer and more targeted sales pitch may lose the viewer's interest.
Although initially used to track parts in vehicle manufacturing, QR codes are used over a much wider range of applications, including commercial tracking, entertainment and transport ticketing, product and loyalty marketing (examples: mobile couponing where a company's discounted and percent discount can be captured using a QR code decoder which is a mobile app, or storing a company's information such as address and related information alongside its alpha-numeric text data as can be seen in Yellow Pages directory), and in-store product labeling. It can also be used in storing personal information for use by organizations. An example of this is Philippines National Bureau of Investigation (NBI) where NBI clearances now come with a QR code. Many of these applications target
mobile-phoneusers (via
mobile tagging). Users may receive text, add a
vCard contact to their device, open a URI, or compose an
e-mailor text message after scanning QR codes. They can generate and print their own QR codes for others to scan and use by visiting one of several pay or free QR code-generating sites or apps.
Google had an
API, now deprecated, to generate QR codes,
[11] and apps for scanning QR codes can be found on nearly all smartphone devices.
[12]
QR codes storing addresses and URLs may appear in magazines, on signs, on buses, on business cards, or on almost any object about which users might want information. Users with a
camera phone equipped with the correct reader application can scan the image of the QR code to display text, contact information, connect to a
wireless network, or open a web page in the telephone's browser. This act of linking from physical world objects is termed
hardlinking or
object hyperlinking. QR codes also may be linked to a location to track where a code has been scanned. Either the application that scans the QR code retrieves the geo information by using GPS and cell tower triangulation (aGPS) or the URL encoded in the QR code itself is associated with a location.
[13]

QR codes have been used and printed on train tickets in China since 2010.
[14]
Recruiters have started placing QR codes in job advertisements,
[15] while applicants have started sporting it in their CVs and visiting cards.
[15]
In June 2011 The
Royal Dutch Mint (
Koninklijke Nederlandse Munt) issued the world's first official coin with a QR code to celebrate the centenary of its current building and premises. The coin can be scanned by a
smartphoneand link to a special website with contents about the historical event and design of the coin.
[16] In 2014 the Central Bank of Nigeria issued a 100-naira banknote to commemorate its centennial, the first banknote to incorporate a QR code in its design. When scanned with an internet-enabled mobile device, the code goes to a website which tells the centenary story of Nigeria.
[17] In 2015, the
Central Bank of the Russian Federation issued a 100-ruble note to commemorate the annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation. It contains a QR code into its design, and when scanned with an internet-enabled mobile device, the code goes to a website that details the historical and technical background of the commemorative note. In 2008, a Japanese stonemason announced plans to engrave QR codes on gravestones, allowing visitors to view information about the deceased, and family members to keep track of visits.
[18]
Psychologist
Richard Wiseman was one of the first authors to include QR codes in a book, in
Paranormality: Why We See What Isn't There (2011), allowing his readers to follow-up on
paranormal claims by accessing his research through the codes.
[19]
Mobile operating systems[edit]
QR codes can be used on various mobile device operating systems. These devices support
URL redirection, which allows QR codes to send
metadata to existing applications on the device. Many paid or free apps are available with the ability to scan the codes and hard-link to an external URL.
URLs aided
marketing conversion rates even in the pre-smartphone era, but during those years faced several limitations: ad viewers usually had to type the URL and often did not have a web browser in front of them when they first viewed the ad. The chances were high that they would forget to visit the site later, not bother to type a URL, or forget what URL to type.
Semantic URLs decreased these risks but did not eliminate them. Some of these disadvantages to URL conversion rates are fading away now that smartphones are putting web access and voice recognition in constant reach, with QR code providing the URL for instant access.
Virtual stores[edit]
During the month of June 2011, according to one study, 14 million mobile users scanned a QR code or a barcode. Some 58% of those users scanned a QR or barcode from their homes, while 39% scanned from retail stores; 53% of the 14 million users were men between the ages of 18 and 34.
[20] The use of QR codes for "virtual store" formats started in South Korea,
[21] and Argentina,
[22] but is currently expanding globally.
[23] Walmart, Procter & Gamble and Woolworths have already adopted the Virtual Store concept.
[24]
Code payments[edit]
QR codes can be used to store bank account information or credit card information, or they can be specifically designed to work with particular payment provider applications. There are several trial applications of QR code payments across the world.
[25][26]
In November 2012, QR code payments were deployed on a larger scale in the
Czech Republic when an open format for payment information exchange - a
Short Payment Descriptor - was introduced and endorsed by the Czech Banking Association as the official local solution for QR payments.
[27]
QR codes are commonly used in the field of cryptographic currencies, particularly those based off and including
Bitcoin.
[28]Payment addresses, cryptographic keys and transaction information are often shared between digital wallets in this way.
[29]
Website login[edit]
QR codes can be used to log in into websites: a QR code is shown on the login page on a computer screen, and when a registered user scans it with a verified smartphone, they will automatically be logged in. Authentication is performed by the smartphone which contacts the server. Google tested such a login method in January 2012.
[30]
Funerary use[edit]
In 2008, Ishinokoe in Yamanashi Prefecture, Japan began to sell tombstones with QR codes produced by IT DeSign, where the code leads to a virtual grave site of the deceased.
[31][32][33] Other companies have begun implementing QR codes into tombstones
[34] and in 2014 the
Jewish Cemetery of La Paz in Uruguay, began implementing QR codes for tombstones.
[35]
Encryption[edit]

Japanese immigration stamp with a QR code (content is encrypted)
Encrypted QR codes, which are not very common, have a few implementations. An
Androidapp,
[36] for example, manages encryption and decryption of QR codes using the
DES algorithm(56 bits).
[37] The Japanese immigration system uses encrypted QR codes on landing permission stamps in passports
[38][better source needed] as shown in the figure to the right.
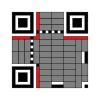
Unlike the older, one-dimensional barcodes that were designed to be mechanically scanned by a narrow beam of light, a QR code is detected by a 2-dimensional digital
image sensor and then digitally analyzed by a programmed processor. The processor locates the three distinctive squares at the corners of the QR code image, using a smaller square (or multiple squares) near the fourth corner to normalize the image for size, orientation, and angle of viewing. The small dots throughout the QR code are then converted to binary numbers and validated with an error-correcting algorithm.
Storage[edit]
The amount of data that can be stored in the QR code symbol depends on the datatype (
mode, or input character set), version (1, …, 40, indicating the overall dimensions of the symbol), and
error correction level. The maximum storage capacities occur for 40-L symbols (version 40, error correction level L):
[4][39]Maximum character storage capacity (40-L)
character refers to individual values of the input mode/datatype
| Input mode | max. characters | bits/char | possible characters, default encoding |
|---|
| Numeric only | 7,089 | 3⅓ | 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 |
|---|
| Alphanumeric | 4,296 | 5½ | 0–9, A–Z (upper-case only), space, $, %, *, +, -, ., /, : |
|---|
| Binary/byte | 2,953 | 8 | ISO 8859-1 |
|---|
| Kanji/kana | 1,817 | 13 | Shift JIS X 0208 |
|---|
Here are some sample QR code symbols:
Version 1 (21×21). Content: "Ver1"
Version 2 (25×25). Content: "Version 2"
Version 3 (29×29). Content: "Version 3 QR Code"
Version 4 (33×33). Content: "Version 4 QR Code, up to 50 char"
Version 10 (57×57). Content: "VERSION 10 QR CODE, UP TO 174 CHAR AT H LEVEL, WITH 57X57 MODULES AND PLENTY OF ERROR CORRECTION TO GO AROUND. NOTE THAT THERE ARE ADDITIONAL TRACKING BOXES"
Version 25 (117×117 enlarged to 640x640)
Version 40 (177×177). Content: 1,264 characters of ordinary/ASCII text: A description of QR codes taken from an early version of this Wikipedia article
Error correction[edit]

Damaged but still decodable QR code

Example of a QR code with artistic embellishment that will still scan correctly thanks to error correction
Codewords are
8 bits long and use the
Reed–Solomon error correction algorithm with four error correction levels. The higher the error correction level, the less storage capacity. The following table lists the approximate error correction capability at each of the four levels:
| Level L (Low) | 7% of codewords can be restored. |
| Level M (Medium) | 15% of codewords can be restored. |
| Level Q (Quartile)[40] | 25% of codewords can be restored. |
| Level H (High) | 30% of codewords can be restored. |
In larger QR symbols, the message is broken up into several Reed–Solomon code blocks. The block size is chosen so that at most 15 errors can be corrected in each block; this limits the complexity of the decoding algorithm. The code blocks are then interleaved together, making it less likely that localized damage to a QR symbol will overwhelm the capacity of any single block.
Due to error correction, it is possible to create artistic QR codes that still scan correctly, but contain intentional errors to make them more readable or attractive to the human eye, as well as to incorporate colors, logos, and other features into the QR code block.
[41][42]
It is also possible to design artistic QR codes without reducing the error correction capacity by manipulating the underlying mathematical constructs.
[43][44]
Encoding[edit]
The format information records two things: the error correction level and the mask pattern used for the symbol. Masking is used to break up patterns in the data area that might confuse a scanner, such as large blank areas or misleading features that look like the locator marks. The mask patterns are defined on a grid that is repeated as necessary to cover the whole symbol. Modules corresponding to the dark areas of the mask are inverted. The format information is protected from errors with a
BCH code, and two complete copies are included in each QR symbol.
[2]
The message dataset is placed from right to left in a zigzag pattern, as shown below. In larger symbols, this is complicated by the presence of the alignment patterns and the use of multiple interleaved error-correction blocks.
Meaning of format information
Message placement within a QR symbol
Larger symbol illustrating interleaved blocks
Four-bit indicators are used to select the encoding mode and convey other information. Encoding modes can be mixed as needed within a QR symbol.
Encoding modes
| Indicator | Meaning |
|---|
| 0001 | Numeric encoding (10 bits per 3 digits) |
| 0010 | Alphanumeric encoding (11 bits per 2 characters) |
| 0100 | Byte encoding (8 bits per character) |
| 1000 | Kanji encoding (13 bits per character) |
| 0011 | Structured append (used to split a message across multiple QR symbols) |
| 0111 | Extended Channel Interpretation (select alternate character set or encoding) |
| 0101 | FNC1 in first position (see Code 128 for more information) |
| 1001 | FNC1 in second position |
| 0000 | End of message |
After every indicator that selects an encoding mode is a length field that tells how many characters are encoded in that mode. The number of bits in the length field depends on the encoding and the symbol version.
Number of bits per length field
| Encoding | Ver. 1–9 | 10–26 | 27–40 |
|---|
| Numeric | 10 | 12 | 14 |
|---|
| Alphanumeric | 9 | 11 | 13 |
|---|
| Byte | 8 | 16 | 16 |
|---|
| Kanji | 8 | 10 | 12 |
|---|
Alphanumeric encoding mode stores a message more compactly than the byte mode can, but cannot store lower-case letters and has only a limited selection of punctuation marks, which are sufficient for rudimentary
web addresses. Two characters are coded in an 11-bit value by this formula:
- V = 45 × C1 + C2
Alphanumeric character codes
| Code | Character | Code | Character | Code | Character | Code | Character | Code | Character |
|---|
| 00 | 0 | 09 | 9 | 18 | I | 27 | R | 36 | Space |
| 01 | 1 | 10 | A | 19 | J | 28 | S | 37 | $ |
| 02 | 2 | 11 | B | 20 | K | 29 | T | 38 | % |
| 03 | 3 | 12 | C | 21 | L | 30 | U | 39 | * |
| 04 | 4 | 13 | D | 22 | M | 31 | V | 40 | + |
| 05 | 5 | 14 | E | 23 | N | 32 | W | 41 | – |
| 06 | 6 | 15 | F | 24 | O | 33 | X | 42 | . |
| 07 | 7 | 16 | G | 25 | P | 34 | Y | 43 | / |
| 08 | 8 | 17 | H | 26 | Q | 35 | Z | 44 | : |
Decoding example[edit]
The following images offer more information about the QR code.
Variants[edit]
Micro QR code is a smaller version of the QR code standard for applications where symbol size is limited. There are four different versions (sizes) of Micro QR codes: the smallest is 11×11 modules; the largest can hold 35 numeric characters.
[45]
IQR code is an alternative to existing QR codes developed by Denso Wave. IQR codes can be created in square or rectangular formations; this is intended for situations where a rectangular barcode would otherwise be more appropriate, such as cylindrical objects. IQR codes can fit the same amount of information in 30% less space. There are 61 versions of square IQR codes, and 15 versions of rectangular codes. For squares, the minimum size is 9x9 modules; rectangles have a minimum of 19x5 modules. IQR codes add error correction level S, which allows for 50% error correction.
[46] IQR Codes have not yet been given an ISO specification, and only proprietary Denso Wave products can create or read IQR codes.
[47]
Model 1 QR code is an older version of the specification. It is visually similar to the widely seen model 2 codes, but lacks alignment patterns.
-
Micro QR code functional regions
-
Model 1 QR code functional regions
License[edit]
The use of QR Code technology is freely licensed as long as users follow the standards for QR Code documented with
JISor
ISO. Non-standardized codes may require special licensing.
[48]
Denso Wave owns a number of
patents on QR Code technology, but has chosen to exercise them in a limited fashion.
[48] In order to promote widespread usage of the technology Denso Wave chose to waive its rights to a key patent in its possession for
standardized codes only.
[5] In the USA, the granted QR Code patent is
US 5726435, and in Japan
JP 2938338. The European Patent Office granted patent
"EPO 0672994". to Denso Wave, which was then validated into French, UK, and German patents, all of which are still in force as of November 2011.
The text
QR Code itself is a
registered trademark and
wordmark of Denso Wave Incorporated.
[49] In UK, the trademark is registered as E921775, the word "QR Code", with a filing date of 03/09/1998.
[50] The UK version of the trademark is based on the Kabushiki Kaisha Denso (DENSO CORPORATION) trademark, filed as Trademark 000921775, the word "QR Code", on 03/09/1998 and registered on 6/12/1999 with the European Union OHIM (Office for Harmonization in the Internal Market).
[51] The U.S. Trademark for the word "QR Code" is Trademark 2435991 and was filed on 29 September 1998 with an amended registration date of 13 March 2001, assigned to Denso Corporation.
[52]
The only context in which common QR codes can carry executable data is the
URL data type. These URLs may host JavaScript code, which can be used to exploit vulnerabilities in applications on the host system, such as the reader, the web browser or the image viewer, since a reader will typically send the data to the application associated with the data type used by the QR code.
In the case of no software exploits, malicious QR codes combined with a permissive reader can still put a computer's contents and user's privacy at risk. This practice is known as "attagging", a
portmanteau of "attack tagging".
[53] They are easily created and can be affixed over legitimate QR codes.
[54] On a
smartphone, the reader's permissions may allow use of the camera, full Internet access, read/write contact data,
GPS, read
browser history, read/write local storage, and global system changes.
[55][56][57]
Risks include linking to dangerous web sites with browser exploits, enabling the microphone/camera/GPS, and then streaming those feeds to a remote server, analysis of sensitive data (passwords, files, contacts, transactions),
[58] and sending email/
SMS/IM messages or
DDOS packets as part of a
botnet, corrupting privacy settings, stealing identity,
[59] and even containing malicious logic themselves such as
JavaScript[60] or a virus.
[61][62] These actions could occur in the background while the user is only seeing the reader opening a seemingly harmless web page.
[63] In Russia, a malicious QR code caused phones that scanned it to send premium texts at a fee of US$6 each.
[53]
Extension[edit]

Samples of the High Capacity Colored 2-Dimensional (HCC2D) code: (a) 4-color HCC2D code and (b) 8-color HCC2D code.
Researchers have proposed a new High Capacity Colored 2-Dimensional (HCC2D) Code, which builds upon a QR code basis for preserving the QR robustness to distortions and use colors for increasing data density (at this stage it is still in prototyping phase). The HCC2D code specification is described in details in Querini et al. (2014),
[64] while techniques for color classification of HCC2D code cells are descripted in details in Querini and
Italiano (2014),
[65] which is an extended version of Querini and Italiano (2013).
[66]
Introducing colors into QR codes requires addressing additional issues. In particular, during QR code reading only the brightness information is taken into account, while HCC2D codes have to cope with chromatic distortions during the decoding phase. In order to ensure adaptation to chromatic distortions which arise in each scanned code, HCC2D codes make use of an additional field: the Color Palette Pattern. This is because color cells of a Color Palette Pattern are supposed to be distorted in the same way as color cells of the Encoding Region. Replicated color palettes are used for training machine learning classifiers.
TO SEE THE EFFECTIVENESS OF A QR CODE, SCAN OURS